By definition, supercomputers are the fastest and most
powerful computers available, and at present the term refers to machines with
hundreds of thousands of processors. They are the superstars of the high–performance
class of computers. Personal computers (PCs) small enough in size and cost to
be used by an individual, yet powerful enough for advanced scientific and
engineering applications, can also be high–performance computers. We define
High Performance Computing as machines with a good balance among the following
major elements:
● Multi staged (pipelined) functional units.
● Multiple central processing units (CPUs) (parallel
machines).
● Multiple cores.
● Fast central registers.
● Very large, fast memories.
● Very fast communication among functional units.
● Vector, video, or array processors.
● Software that integrates the above effectively.
As a simple example, it makes little sense to have a CPU of
incredibly high speed coupled to a memory system and software that cannot keep
up with it.
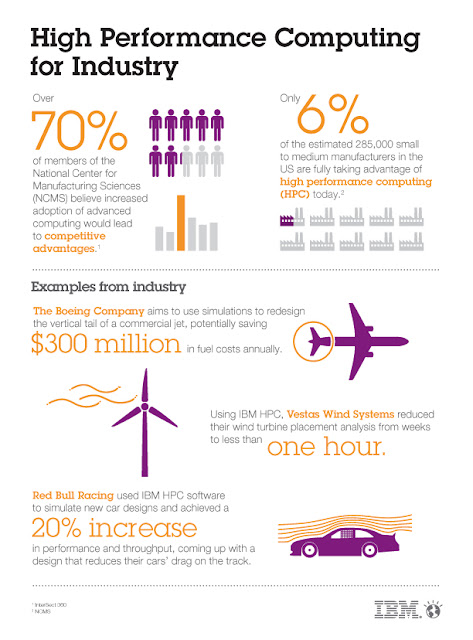
HPC and supercomputers are often associated with large,
government-funded agencies or with academic institutions. However, most High
Performance Computing today is in the commercial sector, in fields such as aerospace,
automotive, semiconductor design, large equipment design and manufacturing,
energy exploration, and financial computing.
HPC is used in other domains in which very large
computations—such as fluid dynamics, electromagnetic simulations, and complex
materials analysis—must be performed to ensure a high level of accuracy and
predictability, resulting in higher quality, and safer, more efficient
products. For example, HPC is used to model the aerodynamics, thermal
characteristics, and mechanical properties of an automotive sub assembly or
components to find exactly the right design that balances efficiency,
reliability, cost, and safety, before spending millions of dollars prototyping
a real product.
 |
| Image Source :- http://ibmdeepcomputing.tumblr.com/image/25850918222 |
HPC is also found in domains such as 2D and 3D rendering for
media and entertainment, genomics and proteomics analysis for life sciences and
healthcare, Oil and gas reservoir simulation for energy exploration, and design
verification for the semiconductor industry. In the financial sector, HPC is
used to perform institutional liquidity simulations and to predict the future
values and risks of complex investments. In architectural design, HPC is used
to model everything from the structural properties of a building, to the
efficiency of its cooling systems under thousands of different input
parameters, resulting in millions of different simulation scenarios.
Over time, the growing use of High Performance Computing in
research and in the commercial sector, particularly in manufacturing, finance,
and energy exploration, coupled with a growing catalog of High Performance
Computing applications, created a trend toward HPC platforms built to handle a
wider variety of workloads, and these platforms are constructed using more
widely available components. This use of commodity hardware components
characterizes the cluster and grid era of High Performance Computing. Clusters
and grids continue to be the dominant methods of deploying High Performance
Computing in both the commercial and research/academic sectors. Economies of
scale, and the need to centrally manage resources across large organizations
with diverse requirements, have resulted in the practical reality that widely
divergent applications are often run on the same, shared HPC infrastructure.
High performance computing can happen on:
● A workstation, desktop, laptop, smartphone!
● A supercomputer
● A Linux/MacOS/Windows/... cluster
● A grid or a cloud
● Cyber infrastructure = any combination of the above
Reference :-
Reference :-


